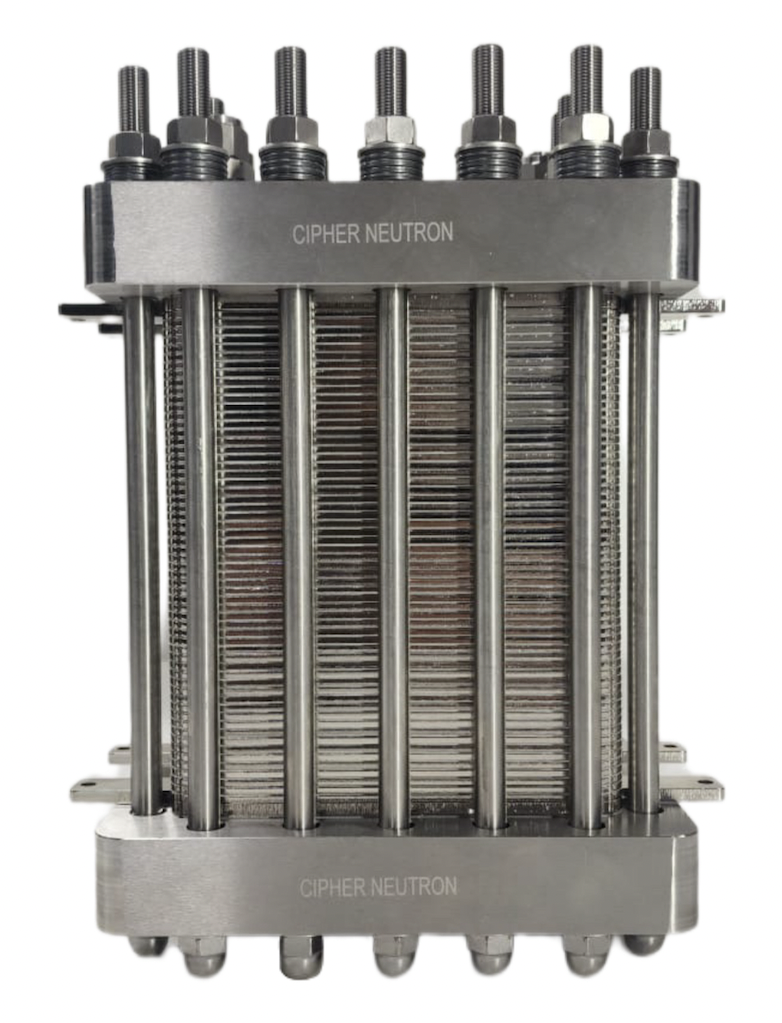


The AEM Electrolyser
Anion Exchange Membrane (AEM) electrolysis stands out as the cutting-edge technology for green hydrogen production. In this process, the Anion Exchange Membrane facilitates the passage of negatively charged hydroxyl ions (OH-) while impeding positively charged ions (H+). The confined protons (H+) combine to form green hydrogen gas on the cathode side, while hydroxyl ions (OH-) on the anode side create water and oxygen gas. The advantages of Anion Exchange Membrane (AEM) electrolysis extend beyond traditional Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) and Alkaline electrolysis technologies.
AEM Electrolysers distinguish themselves by their impressive capability to deliver high-pressure outputs, reaching up to 30 bar, and generating exceptionally pure hydrogen gas with a purity of 99.9%. Noteworthy is the fact that these accomplishments are achieved without relying on supply chain-constrained Platinum Group Metals (PGMs) or the use of harmful and toxic chemicals. This key feature sets AEM Electrolysers apart from other electrolyser technologies available in the market.
The synergy of exceptional efficiency, cost-effectiveness, and sustainability establishes AEM electrolysis as a top-tier option in Green Hydrogen production. Cipher Neutron proudly champions this innovative technology, spearheading advancements that reshape the clean and renewable energy solutions landscape. Additionally, AEMs contribute to prolonged electrolyser lifespan, minimizing the need for repairs and reducing overall process costs. AEM electrolysers boast a compact and scalable design, making them ideal for projects of various sizes.
AEM Electrolyser specifications
- Sustainable
- Affordable
- Longer Lifetime
- Environment Friendly
- Hydrogen pressure Up to 30 bar
- Hydrogen purity without additional purification Up to 99.9 %
- Hydrogen purity with additional purification Up to 99.999 %
- Feed water quality ASTM Type 1
- Feed water pressure 2 to 6 bar
- Feed water temperature 5° C to 40° C
- Nominal power consumption, beginning of life (BoL)4.54 kWh/Nm3 at stack level
- Amperage at nominal operating voltage, beginning of life (BoL)>700mA/cm2
- Amperage at 2 volts per cell, beginning of life (BoL)>2000mA/cm2
- Average cell voltage at end of life (EoL) 2.2V
- Electrolyte type 1M KOH
- Range of operation 20% to 120%
- Membrane crossover concentration (%)< 0.001 mL/min.cm2
- Ambient operative temperature range5° C to 40° C
- Waste recovery systemoptional
PFAS Free Technology

Health and Environmental Concerns
Indeed, recent attention on PFAS has added an extra layer of complexity to the challenges faced by the green hydrogen industry. PFAS, associated with detrimental health effects such as cancer, birth defects, kidney failure, and other chronic illnesses, has raised significant concerns. Numerous studies have underscored the adverse health impacts of PFAS exposure, particularly emphasizing the vulnerability of developing fetuses, infants, and children.

Industry Impact of PFAS Use:
Compounding the issue, the pervasive nature of these chemicals is evident as they have been detected in the blood of 99% of Americans tested for them. This widespread presence emphasizes the urgent need for alternative technologies and practices in the green hydrogen sector to mitigate environmental and health risks associated with PFAS, ensuring a safer and more sustainable future for the industry.

Regulatory Response and Compliance
The health risks associated with PFAS have raised significant concerns, particularly in the drinking water sector. A 2023 study found over 45% of US tap water contaminated with toxic PFAS. In the green hydrogen industry, PEM electrolysers use PFAS-based membranes, linked to severe health issues like cancer and birth defects. These substances’ persistence in the environment for millennia exacerbates the challenge.
Need for Research and Collaboration
The global reaction to these concerns is evident, with entities like the European Union and the United States considering banning specific PFAS materials. Potential regulatory measures could disrupt the supply chain of the already strained PEM electrolyser industry, leading to a reassessment of materials and technologies in the green hydrogen sector to meet environmental and health safety criteria.
Technology Comparison
| Alkaline | PEM | AEM | |
| Ampacity | Low | High | High |
| Catalyst | PGM Free | PGM Based | PGM Free |
| CAPEX | Low | High | Low |
| H2 Pressure | Low | High | High |
| System Response | Slow | Fast | Fast |
| Maturity | Mature | Mature | Latest |
| Compact design | No | Yes | Yes |
| Grid balancing Response | Poor | Good | Good |

AEM Applications

Chemical Industry

Oil and gas Industry

Mining Industry

Steel Industry

Transportation Industry